inlandWaters
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
Scale
-
NLS-FI INSPIRE Hydrography Theme Dataset is a dataset depicting the Hydrography Physical Waters covering the whole of Finland. It contains the following INSPIRE feature types: Dam Or Weir, Land-water Boundary, Rapids, Shoreline Construction, Standing Water, Watercourse. The elements are updated approximately every 5–10 years. The dataset is based on the NLS Topographic database: https://www.paikkatietohakemisto.fi/geonetwork/srv/eng/catalog.search#/metadata/cfe54093-aa87-46e2-bfa2-a20def7b036f The dataset is available via the NLS-FI INSPIRE Download Service (WFS) for Hydrography Theme and it can be viewed via NLS-FI INSPIRE View Service (WMS) for Hydrography. http://paikkatiedot.fi/so/4dae5686-2a8c-40d8-837f-ce6f5547dba2
-
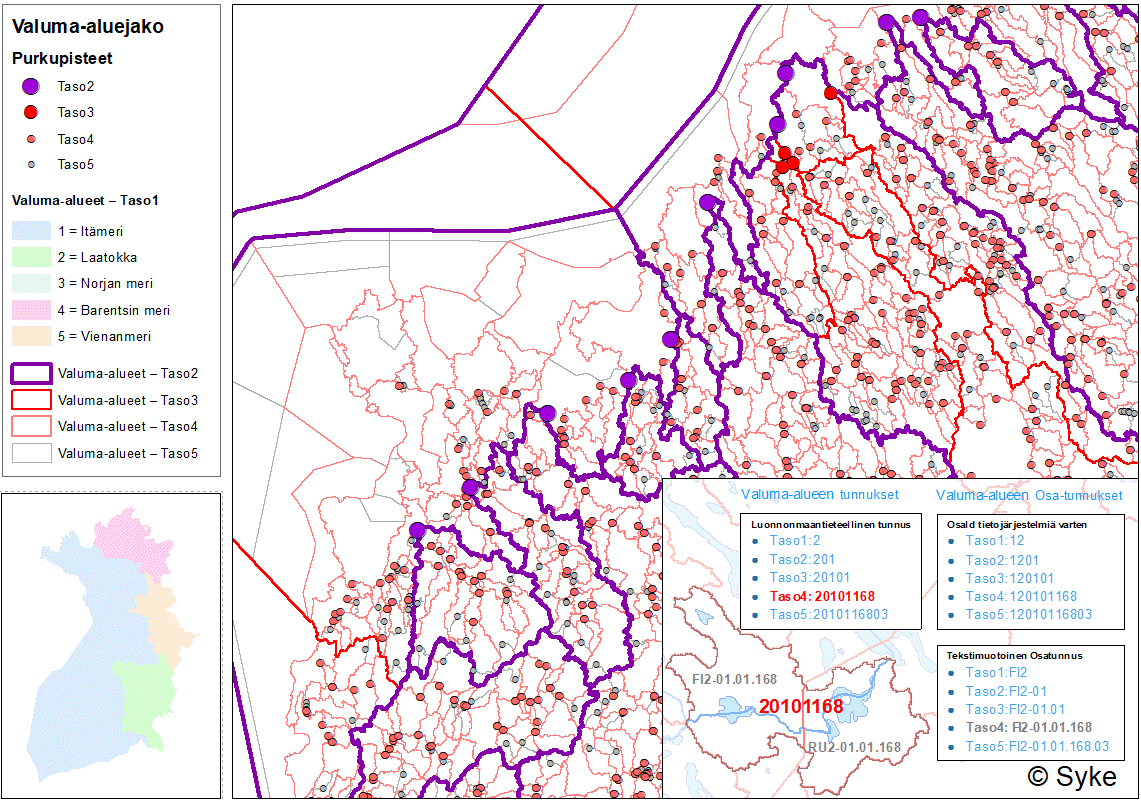
Suomen ympäristökeskuksen (Syke) laatima valtakunnallinen valuma-aluejako koostuu viidestä hierarkiatasosta, jotka kattavat uomien ja järvien valuma-alueiden lisäksi myös merialueet. Tarkimmalla tasolla valuma-aluejaossa on yli 40 000 valuma-aluetta. Valtakunnallinen valuma-aluejako on osa Vesistöjen perustietovarantoa. Valuma-aluejako on tuotettu mallintamalla hyödyntäen Syken laatimaa virtaussuuntamallia, joka perustuu Maanmittauslaitoksen 10 m:n korkeusmalliin. Virtaussuuntamallin virtausreittien tarkkuutta on parannettu kovertamalla siihen uomaverkostoa ja vesialueita sekä yleisten teiden tierummut. Hierarkkisen perustan valtakunnalliselle valuma-aluejaolle luo Syken Ranta10-rantaviiva-aineiston uomaverkosto ja järvet. Valtakunnallinen valuma-aluejako on luotu palvelemaan hyvin laajasti vesivarojen käyttöä ja hoitoa, vesiensuojelua ja vesientutkimusta sekä vesivaroihin liittyvää kansainvälistä ja kansallista raportointia ja tietojärjestelmätyötä. VALUMA-ALUEJAON HIERARKIATASOT Valtakunnallinen valuma-aluejako koostuu viidestä hierarkiatasosta, joita kuvaamaan on kehitetty laajennettavissa oleva hierarkkinen tunnusjärjestelmä. Uomien ja järvien valuma-alueille on määritetty purkupisteet. TASO1 jakautuu viiteen valuma-alueeseen sen mukaan, mihin mereen pintavesi lopulta virtaa. Erityistapauksena myös Laatokka muodostaa oman osa-alueensa, vaikka se lopulta laskeekin Itämereen. TASO2 kuvaa päävesistöalueita ja rannikkoalueita (yli 80 kpl). Yksittäisen päävesistöalueen muodostaa vähintään 200 km2:n kokoinen yhden tai useamman laskujoen kautta mereen purkautuvien sisävesien muodostama kokonaisuus. Rannikkoalueet kattavat myös merialueet merisaarineen. Päävesistöalueiden ja rannikkoalueiden nimet ja numerointi noudattelevat aiempaa valuma-aluejakoa. TASO3 sisältää yli 200 osa-aluetta, jotka on muodostettu hyödyntämällä soveltuvilta osin Valuma-aluejako1990:n I jakovaiheen osa-alueita ja merenhoidon aluejakoa sekä HELCOM:n allasjakoa. TASO4 on valuma-aluejaon tarkin valtakunnallisesti yhtenäiseen uomahierarkiaan perustuva taso. Se muodostuu yli 20 000 osa-alueesta, jotka on mallinnettu Ranta10:n järville ja uomille/uomajatkumoille. Uomajatkumolla tarkoitetaan peräkkäisten uomien ja alle 50 ha järvien muodostamia uoma-järviketjuja. Yli 50 ha:n kokoiset järvet ja yli 100 metrin pituiset uomat/uomajatkumot omaavat oman valuma-alueen. Merialueilla apuna osa-alueiden muodostamisessa ovat olleet Vesistöjen perustietovarannon meriperusyksiköiden lisäksi osin myös VHS-rannikkovesimuodostumat. Tällä tasolla valuma-alueiden koon alarajaksi on määritetty 50 ha eli sitä pienemmät valuma-alueet on yhdistetty aina alapuoliseen valuma-alueeseen. TASO5 on valtakunnallisen valuma-aluejaon tiheäseulaisin taso, jossa valuma-alueita on jaettu edelleen pienempiin osiin myös vesienhoidollisin perustein. Taso 5 koostuu uomille, järville ja merialueille sekä niiden osille mallinnetuista valuma-alueista (yht. yli 40 000 osa-aluetta). Perustan Taso5:n valuma-aluerajauksille luovat pintavesien osia kuvaavat vesistöjen perusyksiköt. Järvien valuma-alueet (yli 12 000 kpl) on määritetty yli 1 ha:n järviperusyksiköille uomaverkoston varrella sekä yli 50 ha:n järviperusyksiköille uomaverkoston ulkopuolella. Uomien valuma-alueet (yli 28 000 kpl) on määritetty yli 100 m pituisille uomaperusyksiköille. Meri- ja rannikkoalueiden osa-alueet (yli 400 kpl) on määritetty meriperusyksiköiden avulla huomioiden rannikon välialueet ja merisaarten vedenjakajat. VALUMA-ALUEIDEN TIEDONHALLINTA Perustan valtakunnalliselle valuma-aluejaolle ja sen tiedonhallinnalle luo Vesistöjen perustietovaranto, joka koostuu uomia, järviä ja merialueita kuvaavista paikkatietoaineistoista sekä niihin liitettävissä olevasta tietovarastosta (VesiPetoDW). Valuma-aluejaon hierarkiatasoihin ja niiden osa-alueisiin liittyvä tietovarasto on tallennettu Vesistöjen perustietovarannon VesiPetoDW-tietokantaan. Vesistöjen perustietovarannon tauluista löytyvät valmiiksi lasketut fysiografiset ja hierarkkiset tiedot on linkitettävissä paikkatietotuotteeseen tunnusten avulla. Myöhemmin tiedot ovat saatavilla myös API-rajapinnan kautta. PUUTTEET JA EPÄTARKKUUDET VALUMA-ALUEJAOSSA Virtaussuuntamallin laskentaan ja valuma-aluejaon mallintamiseen käytetyissä lähtöaineistoissa voi esiintyä paikoin puutteita, epätarkkuuksia tai virheitä, jotka saattavat vaikuttaa valuma-alueiden rajaustuloksiin sekä niiden ominaisuustietojen laskentaan. Erityisesti Suomen rajojen ulkopuolisilla vesistöalueiden osa-alueilla valuma-alueiden rajaukset eivät ole luotettavia lähtöaineiston epätarkkuudesta johtuen. Samoin valuma-alueille lasketut tilastotiedot ovat puutteellisia ulkomaille sijoittuvien osa-alueiden osalta. Aineisto kuuluu SYKEn avoimiin aineistoihin (CC BY 4.0). Aineistosta on julkaistu INSPIRE-tietotuote. LISÄTIETOJA Valuma-aluejaon viitedokumentti https://geoportal.ymparisto.fi/meta/julkinen/dokumentit/Valumaaluejako.pdf Vesistöjen perustietovaranto https://ckan.ymparisto.fi/dataset/vesistojen-perustietovaranto Vesistöjen perusyksiköt https://ckan.ymparisto.fi/dataset/vesistojen-perusyksikot Virtaussuuntamalli10m https://ckan.ymparisto.fi/dataset/virtaussuuntamalli-10-m Ranta10 https://ckan.ymparisto.fi/dataset/ranta10-rantaviiva-1-10-000 Tämä valtakunnallinen valuma-aluejako tulee korvaamaan 1990-luvulla käyttöönotetun valuma-aluejaon. https://ckan.ymparisto.fi/dataset/valuma-aluejako-1990 THE FINNISH RIVER BASIN SYSTEM The Finnish River basin system made by the Finnish Environment Institute (Syke) consists of five hierarchical levels, which cover not only the catchment areas of river segments and lakes, but also sea areas. At the most precise level, there are more than 40,000 catchment areas in the river basin system. The river basin system is part of the Water database. The river basin system has been produced by modeling using the flow direction model prepared by Syke, which is based on the 10 m digital elevation model (DEM) of the National Land Survey of Finland. The accuracy of the flow paths of the flow direction model has been improved by burning in the river network and lakes as well as road culverts of public roads. The river network and lakes of Syke’s Ranta10 shoreline data set creates the hierarchical basis for the river basin system. The Finnish River basin system has been created to serve very broadly the use and management of water resources, water protection and water research, as well as international and national reporting and information systems related to water resources. THE HIERARCHY LEVELS OF THE RIVER BASIN SYSTEM The Finnish River basin system consists of five hierarchy levels, including expandable hierarchical identification system. Discharge points have been determined for the catchment areas of rivers and lakes. LEVEL 1 is divided into five catchment areas, depending on which sea the surface water eventually flows into. As a special case, Lake Ladoga also forms its own sub-region, even if it eventually flows into the Baltic Sea. LEVEL 2 describes main watershed areas and coastal areas (more than 80 areas). An individual main river basin is formed by inland waters discharging into the sea through one or more tributaries with a size of at least 200 km2. Coastal areas also cover sea areas with sea islands. The names and numbering of the main watershed areas and coastal areas follow the previous river basin system. LEVEL 3 contains more than 200 sub-areas, which have been formed by utilizing, where applicable, the sub-areas of the 1st level of the previous river basin system, as well as the marine management areas and HELCOM's basin division. LEVEL 4 is the most accurate level of the river basin system based on a nationally uniform river network hierarchy. It consists of more than 20,000 sub-catchments modeled on Ranta10's lakes and river segments. Lakes over 50 ha in size and “river segment continuations” over 100 meters long have their own catchment area. In marine areas, in addition to the marine basic units of the Water database, WFD coastal water bodies have also been used to help in the formation of sub-regions. At this level, the lower limit of the size of the catchment areas has been determined to be 50 ha, i.e. catchment areas smaller than that are always connected to the catchment area below. In LEVEL 5 catchment areas have been further divided into smaller parts also based on WFD water bodies. Level 5 consists of catchment areas modeled for river segments, lakes and sea areas and their parts (over 40,000 parts in total). The basis for Level 5 catchment area delineations are the basic units of the Water database. The catchment areas of the lakes (more than 12,000) have been determined for basic lake units of more than 1 ha along the river network and for basic lake units of more than 50 ha outside the river network. The catchment areas of the river segments (more than 28,000 pieces) have been determined for river basic units longer than 100 m. Sub-areas of sea and coastal areas (more than 400 units) have been defined using marine basic units, taking into account the intermediate areas of the coast and watersheds of sea islands. INFORMATION MANAGEMENT OF CATCHMENTS The basis for the river basin system and its data management is the creation of the Water database of water basic units, which consists of spatial data materials describing river segments, lakes and marine areas, as well as a data warehouse that can be connected to them (VesiPetoDW). The pre-calculated physiographical and hierarchical data found in the tables of the Water database can be linked to the spatial data product using unique Ids. Later, the data will also be available via the API interface. DEFICIENCIES AND INACCURACIES IN THE RIVER BASIN SYSTEM The source materials used for the calculation of the flow direction model and the modeling of the catchment area distribution may have some shortcomings, inaccuracies or errors, which may affect the delineation results of the catchment areas and the calculation of their characteristic data. Especially in sub-regions of watersheds outside the borders of Finland, the delineations of catchment areas are not reliable due to the inaccuracy of the source material. Similarly, the statistical data calculated for catchment areas are incomplete for sub-areas located abroad.
-
Vesienhoidon järjestämisestä annetun lain (1299/2004) 9 §:n mukaan vesienhoitoalueella pintavesien seuranta on järjestettävä niin, että niiden tilasta saadaan yhtenäinen ja monipuolinen kokonaiskuva. Pintavesien ekologinen ja kemiallinen tila luokitellaan seurannasta kerääntyvän aineiston perusteella. Aineisto sisältää ne jokien, järvien ja rannikkovesien (vesimuodostumien) seurantapaikat, jotka raportoitiin virallisesti EU:lle vuonna 2022. Seurantapaikkoja on kattavasti koko Suomen alueella. Seuranta-aineistoa on kertynyt pintavesistä jo 1960-luvulta alkaen ja olemassa olevat havaintopaikat linkitettiin seurantapaikkoihin. Vedenlaatu-, pohjaeläin-, vesikasvi- ja kalaston näytteet otetaan kussakin vesimuodostumassa havaintopaikoilta, jotka on linkitetty vesimuodostuman seurantapaikkaan. Seurantapaikan koordinaatit määrätään vesimuodostuman laskennallisen keskipisteen mukaan tai merkitään samoiksi kuin järvisyvänteen tai rannikkoalueen vedenlaadun pitkäaikainen havaintopaikka. Joessa alueen koordinaatiksi valitaan joen tarkasteluyksikön merkittävin vedenlaadun havaintopaikka. Seurantapaikat kuuluvat joko perusseurantaan tai toiminnalliseen seurantaan tai molempiin. Riittävän monessa pintavesimuodostumassa on tehtävä perusseurantaa, jotta voidaan arvioida vesienhoitoalueen kaikkien valuma-alueiden ja osavaluma-alueiden pintavesien tila kokonaisuudessaan. Toiminnallista seurantaa on tehtävä kaikissa niissä vesimuodostumissa, joiden osalta on joko vaikutusarvioinnin tai perusseurannan mukaan mahdollista, että ympäristötavoitteet jäävät saavuttamatta, tai joihin päästetään prioriteettilistan aineita (haitallisia aineita, jotka on direktiivissä määrätty). Tarkemmat tiedot seurantapaikkojen vedenlaadusta on löydettävissä ympäristöhallinnon Pintavesien tilan tietojärjestelmästä. Aineisto sisältää vuonna 2022 EUlle raportoidut jokien, järvien ja rannikkovesien seurantapaikat. Käyttötarkoitus: Aineisto sisältää EUlle raportoidut jokien, järvien ja rannikkovesien seurantapaikat. Aineisto kuuluu SYKEn avoimiin aineistoihin (CC BY 4.0). Aineistosta on julkaistu INSPIRE-tietotuote. Lisätietoja: http://www.ymparisto.fi/fi-FI/Vesi/Pintavesien_tila/Pintavesien_tilan_seuranta https://geoportal.ymparisto.fi/meta/julkinen/dokumentit/VHS_seurantapisteet.pdf According to 9 § of the Act on the Organization of Water Management (1299/2004), the monitoring of surface waters in a River Basin District (RBD) must be organized in such a way that a uniform and diverse overall picture of their status is obtained. The ecological and chemical status of surface waters is classified on the basis of data collected from monitoring. The data includes those monitoring sites for rivers, lakes and coastal waters (water bodies) that were officially reported to the EU in 2022. There are monitoring sites comprehensively throughout Finland. Monitoring data have been accumulated from surface waters since the 1960s and existing observation sites were linked to monitoring sites. Samples for water quality, benthic fauna, aquatic plants and fish in each water body are taken from observation sites linked to a water body monitoring site. The coordinates of the monitoring site are determined according to the calculated center of the water body or are marked as the same as the long-term observation point for water quality in the lake basin or coastal area. In the river, the monitoring site has usually the same coordinates as the most significant water quality observation point of each river water body. Monitoring sites include either surveillance monitoring or operational monitoring, or both. A sufficient number of surface water bodies must be subject to basic monitoring in order to assess the status of all surface waters in all catchment areas and sub-catchments in the RBD. Operational monitoring must be carried out in all water bodies for which, according to either the impact assessment or the surveillance monitoring, it is possible that environmental objectives will not be met or to which priority list substances (harmful substances provided for in the Directive) will be released. Investigative monitoring is needed in some special cases. More detailed information on the water quality of the monitoring sites can be found in the Environmental Administration's Surface Water Status Information System. The data includes river, lake and coastal water monitoring sites reported to the EU in 2022. This Syke’s dataset can be used according to open data license (CC BY 4.0). INSPIRE compatible dataset has been published.
-
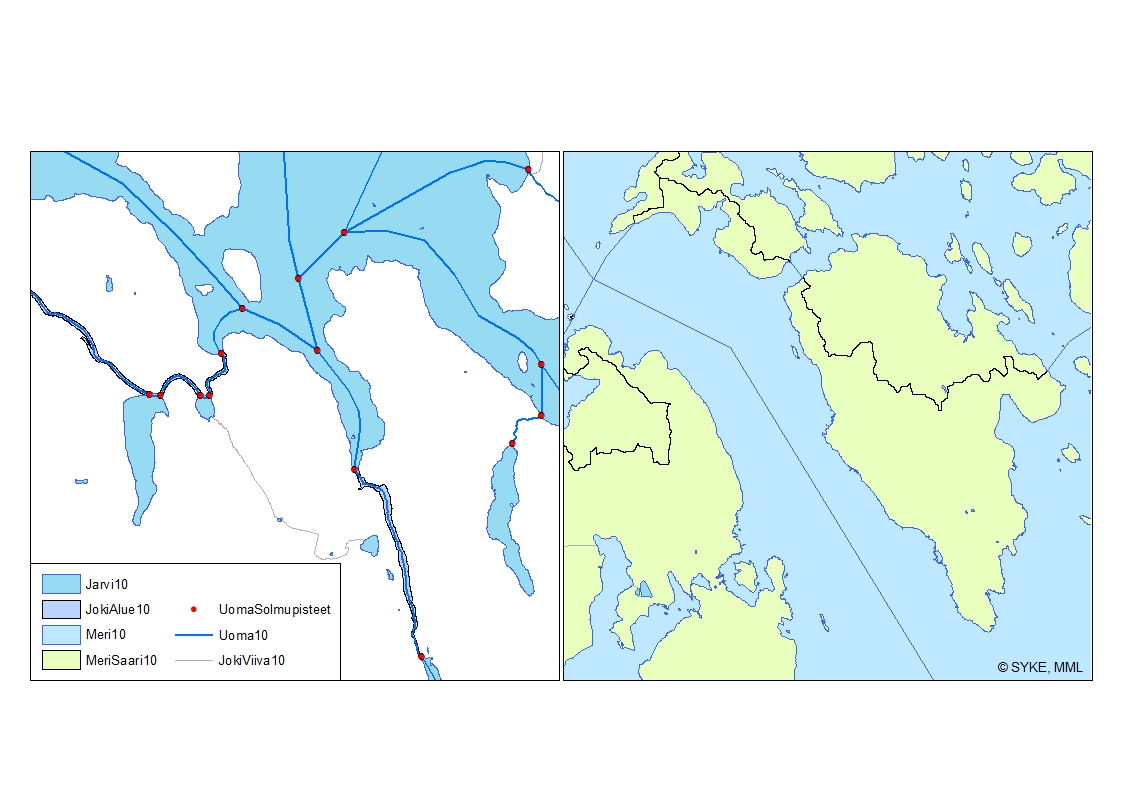
Uomaverkosto pohjautuu Maanmittauslaitoksen maastotietokannan vuosien 2000-2008 aineistoon (1:5 000-1:10 000). Aineiston pohjalta on Sykessä luotu uomia kuvaava uomaverkosto, jonka verkostomainen rakenne on tuotettu lisäämällä viivamaisiin jokiin aluemaisten jokien keskilinjat sekä järvien ylitykset ns. pseudouomilla. Aineistoon on lisätty uomatunnukset. Uomaverkosto kattaa kaikki vähintään yli 10 km2 yläpuolisen valuma-alueen omaavat uomat. Lisäksi uomaverkosto sisältää myös vesienhoidollisesti merkittäviä alle 10km2 yläpuolisen valuma-alueen omaavia uomia. Uomaverkosto ei sinällään kuvaa uuden vesilain vesistömääritelmän mukaista vesistöä. Uoma vaihtuu toiseksi yksilöllisen uomatunnuksen omaavaksi uomaksi aina uomaverkostoon kuuluvien uomien risteyksessä sekä uoman ja järven yhtymäkohdassa. Uomaverkosto on rakennettu siten, että kaikki siihen kuuluvat osat liittyvät topologiset yhteen ja omaavat oikean virtaussuunnan ja sitä voidaan käyttää erilaisiin verkostoanalyyseihin. Uomien välisiä topologia suhteita kuvaavat tiedot on tallennettu erillisiin tauluihin. Uomille on lisäksi laskettu muita paikantavia ja fysiograafisia tietoja. Uomaverkosto kuuluu Syken avoimiin aineistoihin (CC BY 4.0). Uomaverkosto-aineistosta on julkaistu INSPIRE-tietotuote. Käyttötarkoitus: Uomaverkosto on luotu palvelemaan hyvin laajasti vesivarojen käyttöä ja hoitoa, vesiensuojelua ja vesientutkimusta sekä vesivaroihin liittyvää kansainvälistä ja kansallista raportointia ja tietojärjestelmätyötä. Lisätietoja: https://geoportal.ymparisto.fi/meta/julkinen/Dokumentit/ranta10.pdf https://ckan.ymparisto.fi/dataset/ranta10-rantaviiva-1-10-000 River Network River network is based on the topographic database of the National Land Survey of Finland in scale of 1:5 000-1:10 000 from years 2000-2008. The continuous network has been created in Finnish Environment Institute (Syke) by combining rivers to the central lines through polygon rivers and lakes. The dataset includes also unique river codes and lake codes. The river network includes all river segments with catchment areas larger than 10 km². Other, smaller rivers with smaller catchment areas are also included in case they are considered significant for water management tasks (e.g. WFD). The change from one river segment to another, with unique river code and information, is located at the junction of the river network. The river code also changes at a connection point of a river segment and a lake. The river network has been created such a way that all parts of the network are linked topologically to each other and have a correct flow direction so that the dataset can be used for analyzing the network. River network is dataset owned by Syke and has same copyright and ownership conditions as other similar datasets owned by Syke. Syke applies Creative Commons By 4.0 International license for open datasets. River network is developed to serve a wide variety of tasks related to water management, scientific research, water conservation and national and international reporting as well as associated information management.
-
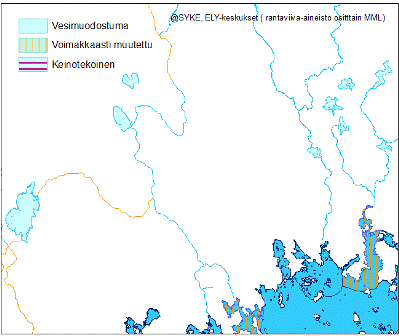
Vesipuitedirektiivin (Euroopan parlamentin ja neuvoston direktiivi 2000/60/EY,23.10.2000) mukaisella pintavesimuodostumalla tarkoitetaan pintavesien erillistä ja merkittävää osaa, kuten järveä, tekoallasta, puroa, jokea tai kanavaa, puron, joen tai kanavan osaa, jokisuun vaihettumisaluetta tai rannikkovesien osaa. Pohjavesimuodostumalla tarkoitetaan. Direktiivin mukaan pohjavesimuodostumalla tarkoitetaan yhtenäisenä vesimassana akviferiin tai akvifereihin varastoitunutta pohjavettä. Pintavedet jaotellaan vesienhoidon järjestämiseksi maantieteellisten ja luonnontieteellisten ominaispiirteiden mukaan tyyppeihin. Pintavedet voidaan nimetä tietyin edellytyksin keinotekoisiksi tai voimakkaasti muutetuiksi. Pintavesimuodostumat kuuluvat johonkin seuraavista jaotteluryhmistä: järvi, joki ja rannikkovesi. Sama vesimuodostuma ei voi kuulua useaan jaotteluryhmään. Pohjavesimuodostumat käsittävät ympäristöhallinnon kartoittamat ja luokittelemat vedenhankintaa varten tärkeät ja vedenhankintaan soveltuvat pohjavesialueet (eli ns. 1- ja 2-luokan pohjavesialueet) sekä E-lisämääreen saaneet pohjavesialueet (1E-, 2E- ja E-luokat), joiden pohjavedestä pintavesi- tai maaekosysteemi on suoraan riippuvainen. Tämä aineisto sisältää pinta- ja pohjavesimuodostumat. Vesimuodostumien rajauksia on tarkistettu suunnittelukausittain. Ympäristöhallinnon sisäisessä käytössä ovat aineistot kolmelta suunnittelukaudelta. Syken Avoin tieto -palvelussa on jaossa toisen ja kolmannen suunnittelukauden aineistot. Aineisto kuuluu SYKEn avoimiin aineistoihin (CC BY 4.0). 3. suunnittelukauden aineistosta on julkaistu INSPIRE-tietotuote. Lisätietoja: https://geoportal.ymparisto.fi/meta/julkinen/dokumentit/VHS_vesimuodostumat.pdf http://www.ymparisto.fi/fi-FI/Vesi/Pintavesien_tila Water bodies according to Water Framework Directive This data contains the surface water bodies and the groundwater bodies which both are defined in the Water Framework Directive (Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000). ‘Body of surface water’ means a discrete and significant element of surface water such as a lake, a reservoir, a stream, river or canal, part of a stream, river or canal, a transitional water or a stretch of coastal water. ‘Body of groundwater’ means a distinct volume of groundwater within an aquifer or aquifers. The surface water bodies shall be identified as falling within either one of the following surface water categories - rivers, lakes, transitional waters or coastal waters - or as artificial surface water bodies or heavily modified surface water bodies. For each surface water category, the surface water bodies shall be differentiated according to type. These types are defined using geographical and natural characteristics. The groundwater bodies are divided into areas that are important for water supply, suitable for water supply and/or groundwater bodies whose groundwater a surface water or terrestrial ecosystems are directly dependent on. The boundaries of water bodies have been revised between planning periods. Data from three planning periods are in the internal use of the environmental administration. Syke’s open spatial datasets contains: • Water bodies according to Water Framework Directive (2022) • Water bodies according to Water Framework Directive (Reported in 2016) This Syke’s dataset can be used according to open data license (CC BY 4.0). INSPIRE compatible dataset has been published.
-
NLS Orthophotos are an aerial photo dataset covering the whole of Finland. An orthophoto is a combination of several individual aerial photos. The geometry of the orthophotos corresponds to a map. The aerial photo data set in orthophoto format is available as - the most recent data set consisting of the most recent aerial photos available. The most recent data is usually 1–3 years old. - old aerial photos, consisting of data sets that are older than the most recent data set. The oldest aerial photos were taken in the 1930s. New data is added to the data set continuously. NLS Orthophotos are updated every 3 years (in Northern Lapland 12 years). Different versions of orthophoto products: - Ortophoto - Ortophoto, false colour - Ortophoto, forest ortho - Ortophoto, natural disasters In addition, there is an index map available presenting the year, when the newest photo was taken in each square. The product belongs to the open data of the National Land Survey of Finland.
-
The Topographic database is a dataset depicting the terrain of all of Finland. The key objects in the Topographic database are the road network, buildings and constructions, administrative borders, geographic names, land use, waterways and elevation. Aerial photographs, scanning data and data provided by other data providers are utilised in updating the Topographic database. The updating is done in close cooperation with the municipalities. Field checks in the terrain are also needed to some extent, mostly as regards the classification of features. The topographic database is used in the production of other map products and in various optimisation tasks. The product belongs to the open data of the National Land Survey of Finland.
 Paikkatietohakemisto
Paikkatietohakemisto